Unveiling The Geography Of Siberia: A Journey Through The Vast And Wild Frontier
Apr 09 2025
Ever wondered what lies beyond the icy tundras and dense forests of Siberia? The geography of Siberia is more than just a map; it's a story of extremes, resilience, and untamed beauty. Stretching over 13 million square kilometers, this region holds secrets that have fascinated explorers and scientists for centuries. From its freezing temperatures to its rich biodiversity, Siberia is a land that defies conventional understanding. So, buckle up, because we're diving deep into the heart of this frozen wonderland!
When you think of Siberia, what comes to mind? Vast icy landscapes, endless forests, and a climate that could freeze your socks off, right? But there's so much more to the geography of Siberia than meets the eye. This place is like a giant puzzle, with each piece revealing something new and fascinating about the natural world. Whether you're a geography enthusiast or just someone curious about the unknown, Siberia has something to offer.
What makes the geography of Siberia so captivating is its sheer scale and diversity. From towering mountains to sprawling plains, this region is a testament to the raw power of nature. But it's not just about the physical features; it's also about the people, the wildlife, and the history that has shaped this land over millennia. So, let's embark on this journey and uncover the secrets of Siberia's geography together.
Read also:Understanding Missouri Health Net A Comprehensive Guide To Healthcare Access
Table of Contents
- Introduction to the Geography of Siberia
- Where is Siberia Located?
- The Harsh Climate of Siberia
- Terrain and Landforms
- Major Rivers in Siberia
- Flora and Fauna
- Natural Resources in Siberia
- Human Settlements and Culture
- Environmental Challenges
- The Future of Siberia's Geography
Introduction to the Geography of Siberia
Siberia, the largest region in Russia, covers an astonishing 77% of the country's total land area. Its geography is as diverse as it is daunting, with landscapes ranging from frozen tundras to lush taiga forests. Imagine a place where winter lasts for most of the year, and temperatures can plummet to -68°C (-86°F). Yet, despite its harsh conditions, Siberia is home to some of the world's most unique ecosystems and wildlife.
Exploring the geography of Siberia means delving into a world where nature rules supreme. The region's vastness and isolation have allowed it to remain relatively untouched by human activity, preserving its pristine beauty. But it's not all about the wild; Siberia also boasts rich cultural heritage and a history that dates back thousands of years. So, what exactly makes this place so special? Let's find out!
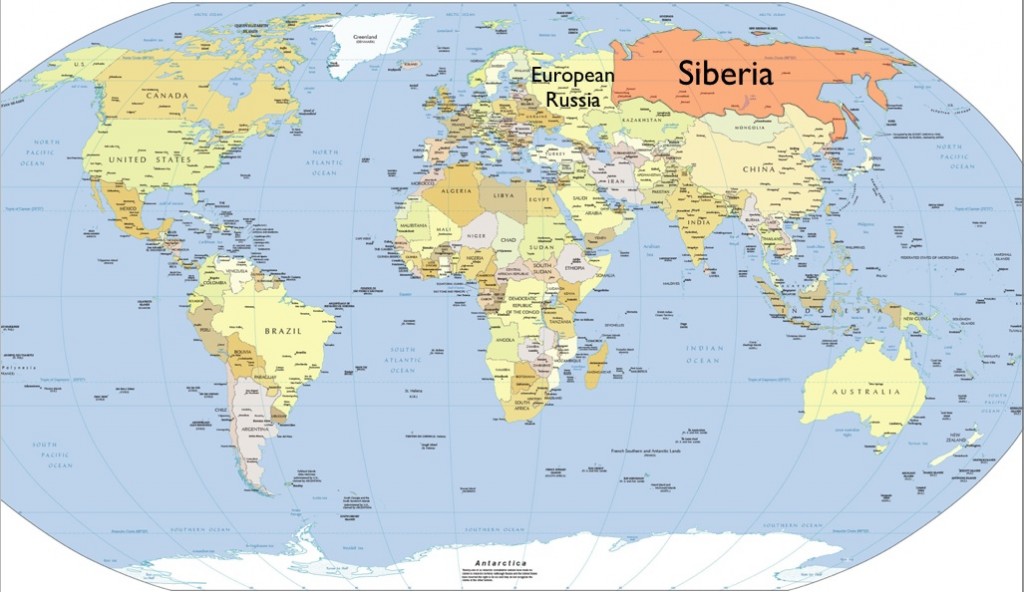
Where is Siberia Located?
Siberia is situated in the northern part of Asia, encompassing a massive portion of the Russian Federation. It stretches from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, and from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the borders of Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and China in the south. This strategic location makes Siberia a crucial link between Europe and Asia, both geographically and culturally.
The region's vastness is mind-boggling. To put it into perspective, Siberia is larger than the entire continent of Australia. And while it may seem like a remote and desolate place, it plays a vital role in global geopolitics, thanks to its abundant natural resources and strategic importance. But don't let the size fool you; Siberia's geography is as complex as it is expansive.
Key Features of Siberia's Location
- Covers 13 million square kilometers
- Shares borders with Kazakhstan, Mongolia, and China
- Extends from the Arctic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean
The Harsh Climate of Siberia
When it comes to the geography of Siberia, you can't ignore the climate. This region is infamous for its extreme weather conditions, with temperatures that can range from scorching summers to bone-chilling winters. The coldest inhabited place on Earth, Oymyakon, is located in Siberia, where temperatures have been recorded as low as -67.7°C (-89.9°F).
But the climate isn't all about freezing cold. Siberia also experiences warm summers, with temperatures occasionally reaching up to 30°C (86°F). This seasonal variation creates a unique environment that supports a wide range of plant and animal species. So, while the winters may be harsh, they're balanced by the relatively mild summers, making Siberia a land of contrasts.
Read also:How To Secure Wild Rivers Tickets For An Unforgettable Experience
Climate Zones in Siberia
- Tundra: Found in the northernmost parts, characterized by permafrost and sparse vegetation
- Taiga: Dominates the central region, home to dense forests and a variety of wildlife
- Steppe: Located in the southern parts, featuring grasslands and fertile soil
Terrain and Landforms
The geography of Siberia is defined by its diverse terrain and landforms. From towering mountain ranges to sprawling plains, this region is a geological wonder. The Ural Mountains mark the western boundary of Siberia, while the Altai Mountains rise in the south. In between, you'll find vast expanses of taiga forests, tundra, and steppe.
One of the most fascinating features of Siberia's geography is its extensive river systems. These rivers not only shape the landscape but also play a crucial role in the region's economy and culture. The Ob, Yenisei, and Lena rivers are among the longest in the world, providing vital transportation routes and supporting a variety of aquatic life.
Major Landforms in Siberia
- Ural Mountains: Separates Europe from Asia
- Altai Mountains: Known for their stunning peaks and rich biodiversity
- Central Siberian Plateau: A vast elevated plain covering much of the region
Major Rivers in Siberia
Rivers are the lifeblood of Siberia, shaping its geography and supporting its ecosystems. The three main rivers—the Ob, Yenisei, and Lena—are some of the longest in the world, stretching thousands of kilometers across the region. These rivers not only provide water for the local populations but also serve as important transportation routes, connecting remote areas to the rest of the world.
During the summer months, these rivers become bustling highways, with boats and barges carrying goods and people. But when winter sets in, they freeze over, creating natural ice roads that are used for transportation. This unique relationship between humans and nature is a defining feature of Siberia's geography.
Key Facts About Siberia's Rivers
- Ob River: Second-longest river in Asia
- Yenisei River: Largest river flowing into the Arctic Ocean
- Lena River: Home to diverse aquatic life
Flora and Fauna
The geography of Siberia is home to a rich variety of flora and fauna, adapted to survive in some of the harshest conditions on Earth. The taiga forests, which cover much of the region, are dominated by coniferous trees such as pine, spruce, and fir. These forests provide habitat for a wide range of wildlife, including bears, wolves, and Siberian tigers.
In the northern tundra, the vegetation is sparse, consisting mainly of mosses, lichens, and hardy shrubs. Despite the harsh conditions, this region supports a surprising number of animal species, including reindeer, arctic foxes, and snowy owls. The steppe areas in the south, with their fertile soil, are ideal for agriculture and grazing, supporting a different set of flora and fauna.
Unique Wildlife of Siberia
- Siberian Tiger: The largest subspecies of tiger
- Reindeer: Native to the tundra regions
- Arctic Fox: Known for its thick white fur
Natural Resources in Siberia
Siberia's geography is rich in natural resources, making it a vital part of the global economy. The region is home to vast reserves of oil, natural gas, and minerals, including gold, diamonds, and coal. These resources have fueled Russia's industrial growth and continue to play a crucial role in the country's economic development.
However, the extraction of these resources comes with its own set of challenges. The harsh climate and remote locations make mining and drilling operations difficult and costly. Additionally, the environmental impact of resource extraction is a growing concern, as it threatens the delicate ecosystems of Siberia.
Key Resources Found in Siberia
- Oil and Natural Gas: Major contributors to Russia's economy
- Gold and Diamonds: Valuable minerals found in the region
- Coal: Used for energy production
Human Settlements and Culture
Despite its harsh conditions, Siberia has been home to human settlements for thousands of years. The indigenous peoples of Siberia, such as the Yakuts, Evenks, and Nenets, have developed unique cultures and traditions that reflect their close relationship with the land. These communities rely on hunting, fishing, and herding for their livelihoods, adapting to the challenging environment in remarkable ways.
Today, Siberia is home to millions of people, with cities like Novosibirsk and Irkutsk serving as major hubs of economic and cultural activity. The region's rich history and diverse population have created a vibrant cultural tapestry, blending traditional practices with modern influences.
Cultural Highlights of Siberia
- Yakutia: Known for its traditional festivals and crafts
- Baikal Region: Famous for its stunning natural beauty
- Novosibirsk: A major center for science and innovation
Environmental Challenges
The geography of Siberia faces numerous environmental challenges, from climate change to deforestation. The region's vast forests are under threat from logging and wildfires, while melting permafrost is altering the landscape and releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These changes have far-reaching implications, not just for Siberia but for the entire planet.
Efforts are being made to address these challenges, with initiatives focused on sustainable resource management, conservation of biodiversity, and reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. However, much more needs to be done to ensure the long-term health and viability of Siberia's ecosystems.
Key Environmental Issues
- Deforestation: Threatens the taiga forests
- Melting Permafrost: Releases methane and carbon dioxide
- Wildfires: Devastate large areas of land
The Future of Siberia's Geography
As the world continues to grapple with the impacts of climate change, the geography of Siberia will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future. The region's vast resources and strategic location make it a key player in global geopolitics, but its fragile ecosystems require careful stewardship to ensure their survival.
Looking ahead, the challenge will be to balance economic development with environmental conservation. This will require collaboration between governments, businesses, and local communities, as well as a commitment to sustainable practices. By working together, we can ensure that Siberia's geography remains a source of wonder and inspiration for generations to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the geography of Siberia is a testament to the power and resilience of nature. From its frozen tundras to its lush forests, this region offers a glimpse into a world that is both harsh and beautiful. By understanding and appreciating the complexities of Siberia's geography, we can better appreciate the challenges and opportunities it presents.
So, what's next? If you found this article informative, why not share it with your friends and family? And if you're curious to learn more about Siberia or any other fascinating geography topics, be sure to check out our other articles. Together, let's continue exploring the wonders of our planet!

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-614400400-5b48d685c9e77c0037d005a0.jpg)